Git Cheatsheet
Git Documentation Github glossary
Commonly Used Commands
Discard the last commit (completely remove the commit from working dir and history)
Throw away all local commits
Download all submodule while cloning the repo
Download all submodules in the repo
Completely remove a file (not only work dir but also in history commits) from the repo and repo history. This is really important if accidentally pushed confidential files like API keys.
git filter-branch --tree-filter 'rm -f my_file' HEAD
git push -f # this changes the entire commit history
Commit and Worktree
Each commit is a file snapshot of the repo, indexed by the a unique hash (SHA, 40 char long checksum hash).
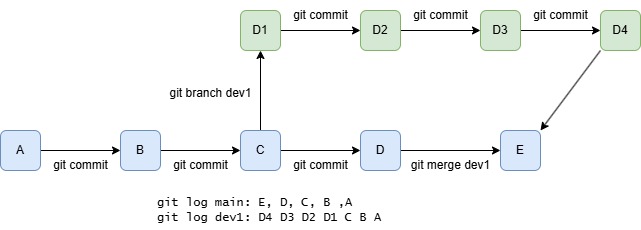
Git history is managed as tree graphs (worktree), each commit is a node of the tree. When creating a new commit with git commit -m "[message]", we create a new node, and its parent is pointing to the previous commit.
branch is a line of development. It can be materialized as a snapshot of the tree. The working tree is associated at most one branch (it might be detached, which is not associated with any named branch), git branch [branch-name] creates such a new branch and git merge [branch-name] merges two branches into one.
HEAD is the reference to the current node (which commit and branch).
branch
Reference Examples
git reset [commit]undoes all commits after [commit], preserving changes locallygit reset --hard [commit]discards all history and back to the specified commitgit revert [commit]create a new commit, which the file changes are reverting the given commit.git branch [branch-name]create a new branchgit checkout [branch-name]switch to the specified branchgit merge [branch-name]combine the specified branch into the current branch.git branch -d [branch-name]delete branchgit tag [tag-name]create a tag from the current commit, usually for tagging specific versions for release.
Basic Commands Reference
Repos and Sync Remote
git initinit repositorygit clone [URL]clone repositorygit fetchdownload the history (without updating the files) from all remote tracking branchesgit mergecombine remote tracking branch into current local branchgit pullupdate current local branch with new commits from corresponding remote branchgit pushupdates all local branch commits to corresponding remote branch
Commit Changes
git add [file]add files to be trackedgit statusshow the working tree statusgit commit -m "[message]"create a commit (a file snapshot)
Inspect History
git loglist commit history for the current branchgit diff [snap1] [snap2]diff the two branches/commitsgit show [commit]outputs metadata and changes of the commit
Configure repo
git config --global user.name "[name]"config the name shown in the git metadata,--globalmeans setup for all repos on this machine.git config --local user.email "[email address]"config the email,--localmeans setup for this repo on this machine only.
.gitignore
Files to be excluded from being tracked (cache, build artifacts, binaries, etc.). Each line is a file pattern to be excluded.
Stash Temporary Changes
git stash maintain a stack of file changes snapshot
git stashsave currently staged changes (without creating a commit) and push the snapshot to the stack, and revert them in the local dirgit stash poppop the stack and write the stashed changes to the local dirgit stash dropdiscard the top of the stack
Submodules
Submodule is to link another repo into the current repo, so that we can use them as a library without copying and syncing their changes.
git submodules is implemented as .gitmodule file, where each entry in
git submodule add [url]add the repo as a submodule to current dir, it can also add specific branch/commit/tag, see thehelpdoc.git submodule update [submodule]update the submodule according to how it is configured.